| [1] Buser D, Dula K, Hess D,et al. Localized ridge augmentation with autografts and barrier membranes.Periodontol 2000. 1999; 19:151-163.[2] Laurie SW, Kaban LB, Mulliken JB,et al.Donor-site morbidity after harvesting rib and iliac bone.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984; 73(6):933-938.[3] Younger EM, Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites.J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3(3):192-195.[4] Arrington ED, Smith WJ, Chambers HG,et al.Complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (329):300-309.[5] Finkemeier CG. Bone-grafting and bone-graft substitutes.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(3):454-464.[6] Colnot C, Romero DM, Huang S, et al. Mechanisms of action of demineralized bone matrix in the repair of cortical bone defects.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(435):69-78.[7] Buck BE, Malinin TI, Brown MD. Bone transplantation and human immunodeficiency virus. An estimate of risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(240):129-136.[8] Buck BE, Resnick L, Shah SM,et al. Human immunodeficiency virus cultured from bone. Implications for transplantation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(251):249-253. [9] Hernigou P, Poignard A, Beaujean F,et al. Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions. Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7):1430-1437.[10] Quarto R, Mastrogiacomo M, Cancedda R,et al. Repair of large bone defects with the use of autologous bone marrow stromal cells.N Engl J Med. 2001;344(5):385-386.[11] Schimming R, Schmelzeisen R.Tissue-engineered bone for maxillary sinus augmentation.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 62(6):724-729.[12] Marcacci M, Kon E, Moukhachev V, et al. Stem cells associated with macroporous bioceramics for long bone repair: 6- to 7-year outcome of a pilot clinical study. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(5):947-955.[13] Hibi H, Yamada Y, Ueda M, et al. Alveolar cleft osteoplasty using tissue-engineered osteogenic material.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;35(6):551-555. [14] Lee J, Sung HM, Jang JD, et al. Successful reconstruction of 15-cm segmental defects by bone marrow stem cells and resected autogenous bone graft in central hemangioma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68(1):188-194. [15] Connolly JF, Guse R, Tiedeman J,et al. Autologous marrow injection as a substitute for operative grafting of tibial nonunions.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(266):259-270. [16] Hernigou P, Poignard A, Beaujean F,et al. Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions. Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7):1430-1437.[17] Fortier LA, Barker JU, Strauss EJ,et al.The role of growth factors in cartilage repair.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(10):2706-2715.[18] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[19] Chang F, Ishii T, Yanai T,et al.Repair of large full-thickness articular cartilage defects by transplantation of autologous uncultured bone-marrow-derived mononuclear cells.J Orthop Res. 2008;26(1):18-26. [20] Tateishi-Yuyama E, Matsubara H, Murohara T,et al.Therapeutic angiogenesis for patients with limb ischaemia by autologous transplantation of bone-marrow cells: a pilot study and a randomised controlled trial.Lancet. 2002;360 (9331):427-435. [21] Rafii S, Lyden D.Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):702-712. [22] Higashi Y, Kimura M, Hara K,et al.Autologous bone-marrow mononuclear cell implantation improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with limb ischemia.Circulation. 2004;109(10):1215-1218. [23] Umemura T, Nishioka K, Igarashi A,et al.Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation induces angiogenesis and bone regeneration in a patient with compartment syndrome.Circ J. 2006;70(10): 1362-1364. [24] Reyes M, Lund T, Lenvik T,et al.Purification and ex vivo expansion of postnatal human marrow mesodermal progenitor cells.Blood. 2001 ;98(9):2615-2625. [25] Yasuhara S, Yasunaga Y, Hisatome T,et al. Efficacy of bone marrow mononuclear cells to promote bone regeneration compared with isolated CD34+ cells from the same volume of aspirate.Artif Organs. 2010;34(7):594-599. [26] Muschler GF, Boehm C, Easley K. Aspiration to obtain osteoblast progenitor cells from human bone marrow: the influence of aspiration volume.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79(11):1699-1709. [27] Soltan M, Smiler DG, Gailani F. A new "platinum" standard for bone grafting: autogenous stem cells.Implant Dent. 2005; 14(4): 322-325.[28] Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T,et al.Concentration of bone marrow total nucleated cells by a point-of-care device provides a high yield and preserves their functional activity. Cell Transplant. 2008;16(10):1059-1069.[29] Thoesen MS, Berg-Foels WS, Stokol T,et al.Use of a centrifugation-based, point-of-care device for production of canine autologous bone marrow and platelet concentrates. Am J Vet Res. 2006;67(10):1655-1661.[30] 尹世昌,焦振华,王功国,等. 浓缩自体骨髓移植配合中药治疗骨不连临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(6):23-25.[31] Jäger M, Herten M, Fochtmann U,et al.Bridging the gap: bone marrow aspiration concentrate reduces autologous bone grafting in osseous defects.J Orthop Res.2011;29(2):173-180. [32] Jäger M, Jelinek EM, Wess KM,et al. Bone marrow concentrate: a novel strategy for bone defect treatment.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009;4(1):34-43.[33] 张远成,刘国辉,茹长英,等.自体浓缩骨髓干细胞复合人工骨植入治疗骨不连[J].中国医药,2010,5(2):158-159.[34] Murawski CD,Duke GL,Deyer TW,et al. Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) as a Biological Adjunct to the Surgical Treatment of Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus.Techniques Foot & Ankle Surg. 2011;10(1):18-27.[35] Adams SB, Lewis JS Jr, Gupta AK,et al. Cannulated screw delivery of bone marrow aspirate concentrate to a stress fracture nonunion: technique tip.Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34(5): 740-744. [36] Smyth NA, Murawski CD, Haleem AM,et al. Establishing proof of concept: Platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow aspirate concentrate may improve cartilage repair following surgical treatment for osteochondral lesions of the talus.World J Orthop. 2012;3(7):101-108.[37] Murawski CD, Kennedy JG. Percutaneous internal fixation of proximal fifth metatarsal jones fractures (Zones II and III) with Charlotte Carolina screw and bone marrow aspirate concentrate: an outcome study in athletes.Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(6):1295-1301.[38] Campbell KJ, Boykin RE, Wijdicks CA,et al. Treatment of a hip capsular injury in a professional soccer player with platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow aspirate concentrate therapy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(7): 1684-1688. [39] Kretlow JD, Spicer PP, Jansen JA, et al. Uncultured marrow mononuclear cells delivered within fibrin glue hydrogels to porous scaffolds enhance bone regeneration within critical-sized rat cranial defects.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 16(12):3555-3568.[40] Rickert D, Sauerbier S, Nagursky H,et al. Maxillary sinus floor elevation with bovine bone mineral combined with either autogenous bone or autogenous stem cells: a prospective randomized clinical trial.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22(3): 251-258.[41] Sauerbier S, Rickert D, Gutwald R,et al. Bone marrow concentrate and bovine bone mineral for sinus floor augmentation: a controlled, randomized, single-blinded clinical and histological trial--per-protocol analysis.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(17-18):2187-2197. |
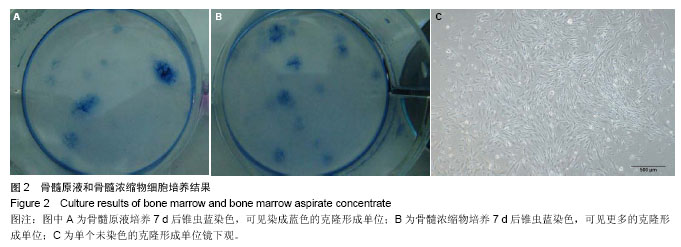

.jpg)
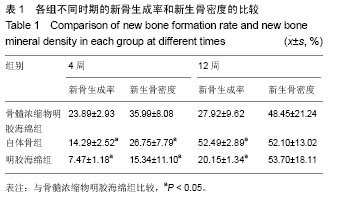
.jpg)